Implantation of a tooth implant
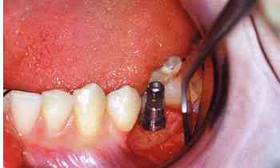
Implantation is a technique of implanting an artificial root in place of a lost tooth.
The implantation of a tooth implant in the jawbone allows you to stop the loss of bone tissue in the place of the missing tooth, as well as solve functional and aesthetic problems.
A dental implant has the same external and quality indicators as a living tooth, so it is indistinguishable from natural teeth, both in sensations and externally. Patients with implants installed do not experience any discomfort.
Implants can be installed instead of one missing tooth or completely restore the entire dentition. Dental implants are used as support for both permanent and removable dentures.
It should be noted that the installation of the implant in the jaw implies the use of modern high-quality equipment and not old milling cutters designed for drilling.
Inaccuracy in work, the use of blunt tools, insufficient cooling can lead to an unsuccessful result.
Implant structure
The implant consists of:
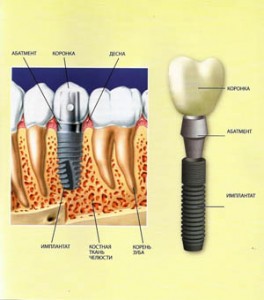
- An implant is a titanium rod implanted in the jaw bone.
- Abutment - the upper part of the structure, which is attached to the implant, after its engraftment. The dental crown is fixed on top of the abutment.
A tooth implant consists of three parts:
- A root immersed in the bone tissue of the jaw.
- Neck - located at the level of the gums.
- The head is a support for the dental crown.
Types of modern implants
- Screw. The root part of the structure is a screw. The implant is implanted in the prepared thread in the jaw bone. One root can replace only one tooth. They are used more often to restore front teeth.
- Lamellar. More often used to replace teeth that perform chewing function. The root section of the implant is a long narrow plate, which is placed in the bone tissue of the jaw for a long distance, which gives it stability.
Materials
For successful implant engraftment, it is necessary that the material from which the artificial root is made is completely inert and does not cause an immune response.
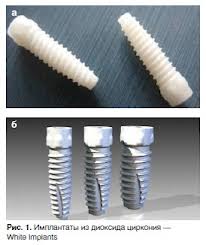
- Most often, alloys of titanium, gold, nickel - chromium - vanadium alloys are used for the manufacture of implants. There are other materials with biocompatibility.
- Stainless steel is considered biotolerant, chromium is a cobalt alloy. Currently, these materials are rarely used, since the service life of structures made from them is very limited.
- The ideal material is ceramics, but, nevertheless, titanium is traditionally considered the best option.
- In recent years, zirconium or alumina has been used to make abutments. strong enough and more esthetic.
These materials are particularly preferred if the patient has an allergic reaction to the metal.
Methodologies
An implant can be implanted in two ways:
- One-step installation. Installation of the implant and abutment is performed simultaneously. This technology avoids repeated surgical exposure. At the time of healing, a temporary crown is fixed, i.e., an immediate functional load is produced.
- Two-stage implantation. First, the implant is implanted in the bone tissue of the jaw, immediately gum is sutured for a period of three to six months, so that the artificial root takes root. After its engraftment, the gum is re-cut and the gum former is installed. After a few weeks, a dental crown is placed.
Ways of carrying out
The surgical stage of an implant implantation operation can be carried out in one of the following ways:
- Using a scalpel. The use of a scalpel is less safe, because the particles of metal from which the scalpel is made may remain on the surface of the implant, which subsequently threatens the emergence of galvanic currents.
- Exposure to the laser beam. The use of a laser ensures bloodlessness and sterility of the operation, as well as high-quality and quick healing of tissues. After the operation, the processing of the surgical field with a semiconductor laser contributes to the rapid engraftment of the implant.
Installation Features
- The place of implantation of the titanium root should correspond as much as possible to the place where the tooth was lost.
- The right choice of design.
- Careful selection of the length and diameter of the implant.
Stages
Implantation of implants is carried out in several stages.
Preparatory

- Examination of the patient.
- Identification of indications and contraindications for surgery.
- If necessary, treatment, rehabilitation of the oral cavity.
- In the case of atrophy of the bone tissue, it builds up.
- If there are relative contraindications to the operation, they are eliminated.
- Implant planning is underway.
Surgical
An operation takes an average of thirty minutes or more, depending on the number of implants to be implanted.
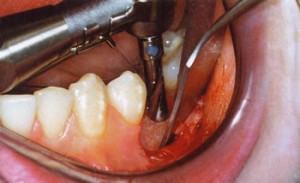
- Local anesthesia is performed.
- Preparation of the surgical field: rinsing the oral cavity with an antiseptic solution, disinfecting the area around the mouth, covering the patient’s body and head with sterile sheets, leaving the area open for surgery.
- The bone is prepared for implantation. The gum is cut, separated from the periosteum.
- Implant bone treatment.
- Drilling a bone with a thin drill to form a place for the installation of a titanium rod of a certain length. Then, the further formation of the implant bed under the implant of a certain shape is performed. For accurate drilling, ready-made templates pre-modeled on a gypsum structure are used. The drilling depth is controlled by a depth gauge. Then, taps are used to create a thread matching the one that the implant has.
- Implant implantation. The implant is screwed into the finished hole using a special tool, at the place where the abutment will be installed in the future, a stub is placed. Such a measure is necessary to prevent the ingrowth of surrounding tissues into the internal threaded channel of the implant.
- Stitching. After the plug is installed, all the incisions made before this are sutured over the implant, i.e. the core is completely submerged under the gingival margin. Periosteal and flaps of the mucous membrane are returned to their original place, and the wound is tightly sutured with interrupted sutures.
Healing
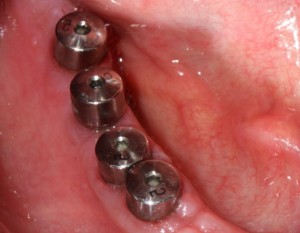
- After healing of the wound surface, sutures are removed.
- The engraftment (osseointegration) of the implant lasts from three to five to six months, and depends on the place of its installation, the characteristics of the bone tissue and the general condition of the body.
- After successful osseointegration, cut the gum and remove the stub. Then the gum shaper is installed.
Implant reinforcement
At this stage:
- Gum shaper removal.
- Abutment installation.
- Taking a cast.
- Further prosthetics.
Postoperative period
- It usually proceeds easily and painlessly.
- Immediately after the operation, you should take a tablet of anesthetic, and you can also drink such a tablet at night. Other medicines, such as antibiotics or antihistamines, are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor.
- After the operation, it is necessary to immediately apply cold to the site of the surgical intervention. This measure will reduce the likelihood of swelling or bruising.
- During the healing period of the gums, you should eat soft, mashed and semi-liquid foods. Hot drinks should not be consumed.
- You can not drive after an operation, as well as perform work associated with increased attention.
- After implantation for several days, it is necessary to avoid physical exertion, hypothermia and overheating.
Installation difficulties
- With insufficient bone, some complications are possible: loosening and prolapse of the implant after one to two years or earlier.
- To prevent this from happening, before implanting, the bone tissue is expanded using a special bone-replacing material.
- Six or more months after the procedure, you can proceed to the implantation of a titanium rod.