Malocclusion
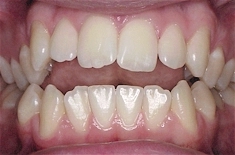
Bite is the interaction of the teeth of the upper and lower rows when they close.
The insufficient development of at least one jaw or the incorrect arrangement of teeth inevitably leads to the formation of a pathological bite.
Varieties of malocclusion are determined by the characteristic closure of the jaws, are examined in the vertical, sagittal and transverse directions.
Depending on the size and position of the jaw bones, the nature of defects in the dentition, the features of jaw closure, the following malocclusions are distinguished:
- Distal bite is a common pathology that is characterized by underdevelopment of the lower jaw or excessive development of the upper jaw. When teeth are closed, the upper frontal teeth are substantially advanced in the forward direction with respect to the lower ones.
- An open bite is an abnormality in which there is no complete or partial closure of the teeth. At the same time, cracks are formed in the place where the jaw is not closed.
- Deep bite - is a common defect in jaw closure, in which the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by more than half the length of the latter.
- Mesial bite is a pathology in which the lower jaw is highly developed and noticeably protrudes forward. And the upper jaw is underdeveloped.
- Cross bite is an anomaly of jaw closure, which is characterized by poor development of one of the sides of any jaw bone.
- Dystopia - is the location of the teeth out of place, which are offset to the side from the normal position.
- Diastema - an abnormal position of the teeth, in which there is a gap in size from 1 to 6 millimeters between the incisors.
Sagittal malocclusion
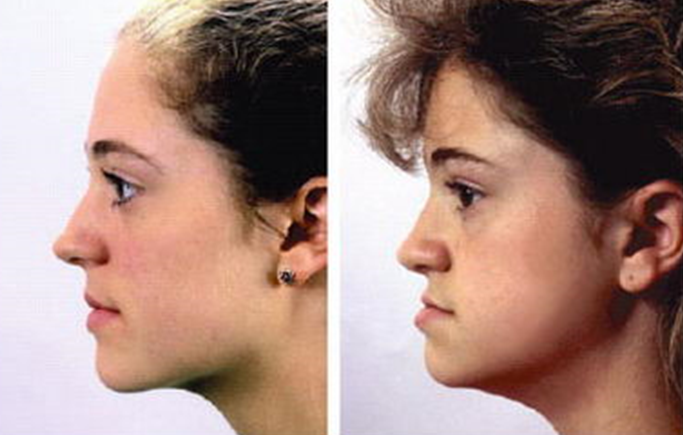
- In the case of sagittal abnormalities, defects in jaw closure occur in the anteroposterior direction.
- This type of pathology includes mesial and distal bites.
- Correction of sagittal malocclusion is aimed at delaying / stimulating the development and growth of the displaced jaw, as well as correcting the area of closure of the upper and lower dentition.
The method of treatment depends on the severity and severity of the pathology, the characteristics of the dentition, as well as the age of the patient.
- During the development of a temporary or intermittent bite, myogymnastics and removable orthodontic constructions are used to correct anomalies.
- For children over twelve years of age and adults, the correction is performed using a bracket system.
- In the presence of anomalies of 2 degrees and above, combined or surgical methods for correcting bites are used.
Vertical anomalies of jaw closure
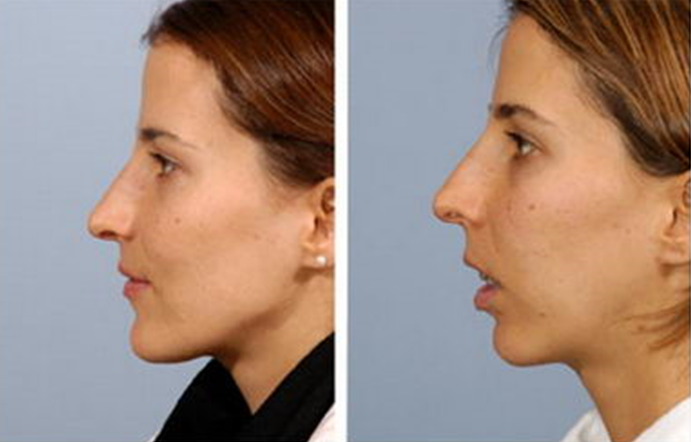
- Defects of the bite in the vertical direction include open and deep bites.
- Such anomalies are characterized by a low or high position of the group of teeth relative to the occlusal surface, as well as dentoalveolar elongation in case of loss or destruction of antagonist teeth.
- Clinical manifestations of vertical anomalies depend on the cause of the defect, localization in the dentition, and the severity of the violations.
One way to correct malocclusion in children is to eliminate etiological factors.
Treatment of vertical anomaly in adults comes down to the use of fixed orthodontic constructions using intermaxillary rubber traction, removable mouthguards, Katz guide crowns, and Engle's arch.
Transverse anomalies
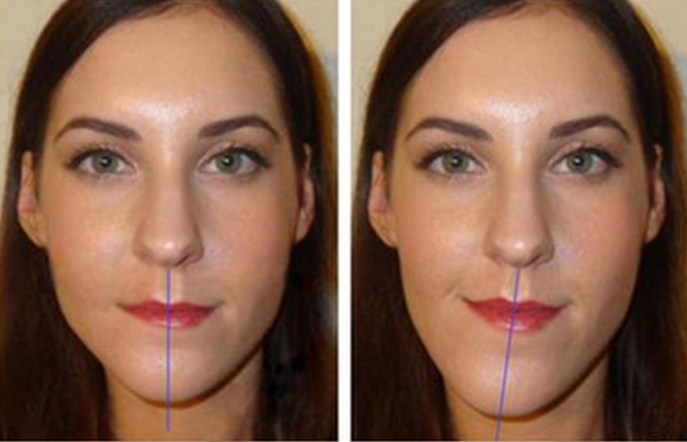
- They are characterized by a mismatch in the width of the upper and lower dentition, or narrowing or lateral displacement of the jaw.
- The group of transversal defect includes cross bite.
Treatment of such a bite should be carried out as soon as possible.
- At the first symptoms of the manifestation of the anomaly, dentition is separated.
- Correction of narrowing of the jaw is carried out using expanding plate devices with screws and springs, activators and regulators of Frenkel functions.
- Sharp defects in jaw closure with complex deformities are corrected by surgical intervention.
Causes of occurrence
The formation of malocclusion may be influenced by several factors:
- Hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of malocclusion pathologists.
- Diseases of a woman during pregnancy.
- The presence of birth injury.
- Chronic diseases of ENT organs at an early age.
- Abuse of a dummy during the period of newborn and early childhood.
- Improper feeding of the baby using nipples.
- Abuse of bad habits at an early age.
- Wrong position of the child in a dream.
- The formation of a child's incorrect posture.
- Rickets disease.
- Loss of primary teeth prematurely.
- The unevenness of the erasure of milk teeth.
- Belated change of primary teeth permanent.
Effects
In addition to aesthetic problems, the wrong bite can bring its owner a lot of health problems.
Any malocclusion has a negative impact on the functioning of the dentition, impaired diction and aesthetics of appearance.
Anomalies of occlusion can lead to such serious consequences as:
- Periodontal disease.
- Chewing function impairment.
- Complications leading to a disease of the temporomandibular joints.
- Partial or full adentia.
- Tooth erasing.
- The presence of speech defects.
- Asymmetry of the shape of the face.
- The presence of problems with prosthetics and dental implants.
- The risk of injury to the tongue, mucous membrane of the gums and cheeks increases.
Pathology of the bite can occur, both independently and in combination with its various forms.
Video: “The consequences of malocclusion”
Diagnostics
- The presence of anomalies in the development of the dentofacial system, the causes of the defect and treatment planning are determined at the reception at the orthodontist during a detailed examination of the patient.
- As an additional study, an X-ray examination of the jaw bones is used.
Treatment
- Correction of the pathology is carried out using orthodontic appliances, which allow you to change the position of the teeth in the row, normalizing the contact of the lower and upper jaws when they close.
- In complex cases, occlusion correction is performed by surgical intervention.
- With severe tooth abrasion, dental prosthetics may be required.
Orthodontic correction of malocclusion anomalies is possible at any age.
However, dentists recommend a correction in childhood until the growth of the jaw bones and teeth is complete.