Biprognathic bite
A bite of teeth is characterized by the ratio of the upper and lower row of teeth with the jaws fully closed.
Bite can be physiological (correct) and pathological (wrong).
There are several varieties of physiological occlusion, but with various variations, the position of the teeth is such that each of them comes into contact with the antagonist tooth of the same name.
- Ideally, each tooth in the upper jaw should be in close contact with the neighboring one.
- In this case, the lower antagonist tooth is usually located slightly behind the upper. Similarly, the teeth of the lower jaw should be closely connected with each other, and the upper similar teeth are in front.
- If, during the closing of the jaws, the frontal upper teeth touch slightly on the lower ones (no more than a third), the molars come into contact with the same teeth on the opposite jaw, then such teeth are considered straight.
Signs of a physiological bite
Correct bite is characterized by the following symptoms:
- There is no crowding of teeth.
- Interdental spaces are not determined.
- When pronouncing, there are no speech defects.
- There is no discomfort when chewing.
- The presence of a slight inclination of the teeth in the oral cavity.
- Conditionally, the central front line coincides with the central part between the upper and lower incisors.
- The presence of the correct shape and the absence of tooth defects.
Kinds
- A direct bite is such a jaw closure when the teeth close with their cutting edges and do not overlap each other. Often this interaction of teeth leads to their increased abrasion.
- The orthognathic bite is the closest to ideal. The upper incisors overlap the lower ones by no more than one third.
- Progenic bite is characterized by a slight extension of the lower jaw forward. This type of tooth closure is on the verge of normal and abnormal.
- A biprognathic bite is such a kind of regular bite, the characteristic features of which are the inclination of the upper and lower incisors towards the vestibule of the mouth with preservation of the cutting-tubercular contact. Since the deviation from the normal state is very insignificant, this relationship of the teeth is within the physiological range.
All of the above types of bite are the norm and are able to provide full functionality of the teeth and aesthetics of appearance.
Video: “Classification of anomalies and occlusion”
Features of a biprognathic bite
- The occurrence of biprognathy is often observed against the background of macroglossia, as well as as a result of the influence of hereditary factors.
- During the period of temporary occlusion, the biprognatic type of closing of the teeth usually does not occur.
- The manifestation of signs is observed at the age of eight to ten years after the permanent incisors erupt.
Treatment
If a pathology of the bipognathic bite is detected, it is necessary to consult an orthodontist in order to correct an existing developmental anomaly.
- If there are diastemas and tremas between the incisors, then elimination the defect is carried out without braces, using plates and vestibular arches on the lower and upper jaw.
- In the presence of crowding of the incisors, after permanent lateral incisors have erupted, occlusion correction is carried out by systematic tooth extraction according to Hotz.
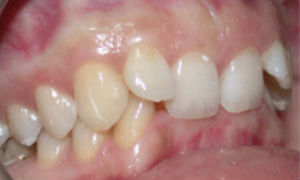
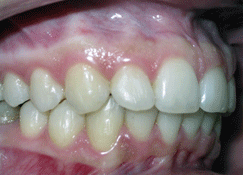
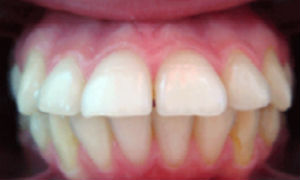
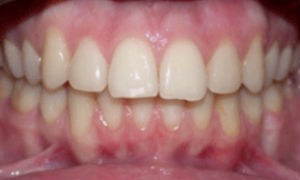
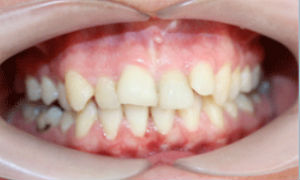
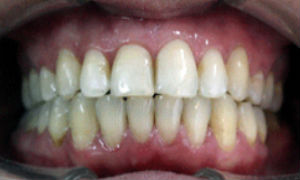
Photo: before and after
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |