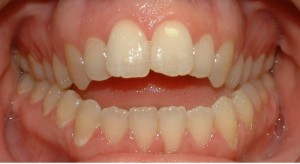
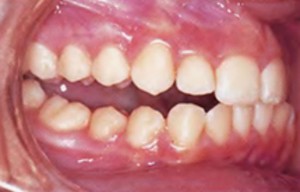
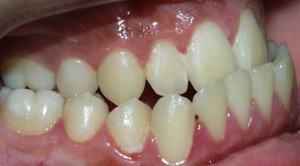
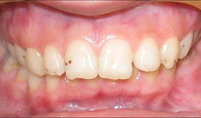
Types of Bites
Teeth bite - This is a feature of closing the teeth of the upper row with the lower.
Dentists use the concept of occlusion as they describe jaw closure.
The position of the jaws, which ends their chewing movement, is called central occlusion.
Thus, a bite is a relationship between the upper dentition and the lower at the time of central occlusion.
What a bite
By the nature of the interaction of the teeth of the upper and lower rows at the time of central occlusion, various occlusion options are determined.
Human bite may be:
- Physiological or correct.
- Malocclusion.
Signs of proper tooth placement:
- Overlapping the upper row of the lower teeth with approximately one third.
- A clear interaction of teeth between antagonists.
- The absence of gaps between the teeth.
- The midline of the face passes between the central incisors of the dentition.
- The absence of violations of the chewing function of teeth and speech.
Varieties of the right bite
In dentistry There are several types of physiological bite:
- The orthognathic bite is considered the standard and is characterized by the fact that the front teeth of the upper row, at the time of jaw closure, overlap the incisors of the lower dentition by about a third of the length of their crowns.
- A direct bite differs in that when the jaws are closed, the upper and lower teeth are connected by cutting edges.
- In the presence of a biprognatic type of occlusion, the incisors of the upper and lower dentition are inclined to the sides of the vestibule of the oral cavity.
- Progenic bite is characterized by a slight extension of the lower jaw in the front direction at the time of closing of the teeth.
Any type of proper bite allows the dentoalveolar system to function fully, while maintaining both the aesthetic appearance of its owner and normal diction.
Video: “What is a right and wrong bite?”
Types of malocclusion
Today, approximately 90% of people suffer from malocclusion.
- This condition contributes to the disruption of the functioning of the dentition and affects the aesthetics of the appearance of a person.
- An incorrect bite can cause diseases of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as other systems and organs.
Abnormal types of malocclusion can be associated with either a genetic predisposition and be inherited from parents or acquired (as a result of various diseases or other factors).
The main indicator of malocclusion is any kind of deviation from the normal state when the dentition closes, up to the absence of occlusion in certain areas.
Depending on the abnormality of the closing of the teeth, a pathological bite can take the following forms:
- Open bite - lack of closing of certain groups of teeth.
- With a deep bite, the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by more than half the crown.
- The distal bite is characterized by underdevelopment, or vice versa, increased development of the lower jaw.
- Cross bite - insufficient unilateral development of any jaw.
- With a mesial bite, a noticeable extension of the lower jaw in the forward direction is noted.
- Dystopia is a pathology that is characterized by the location of individual teeth out of place.
Deep bite
This anomaly is one of the most common bite pathologies. The potential danger of deep bite in the development of psychological discomfort as a result of the presence of aesthetic defects.
Among the other negative consequences for the owner of this anomaly are the following:
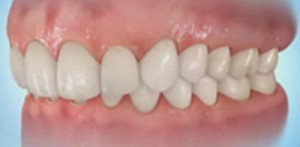
- Difficulty eating.
- Front teeth are subject to high stress.
- Often the oral mucosa is injured.
- Shortening of the lower part of the face, not aesthetic shape of the lips.
- Increased abrasion of the lower incisors, which leads to a violation of the tone of the masticatory muscles. As a result, the temporomandibular joint suffers.
- Crunch, pain, clicking in the temporomandibular joint, gnashing of teeth.
- Frequent headaches.
Effects:
- According to dentists, a deep bite often leads to the appearance of other abnormalities.
- Negative effect on periodontal disease, which leads to the development of periodontal disease and tooth loss.
- Disorders of swallowing and breathing can become a threat to the entire body.
Open bite
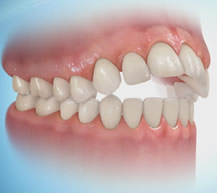
Belongs to the most complex pathology of malocclusion.
Symptoms of anomalies:
- Violation of diction.
- Lengthening the lower part of the face.
- Impaired chewing and swallowing.
- Muscle tension in the mouth.
An open bite can be anterior and lateral, true (rickety) and traumatic.
- The worst option is a rickety type of bite.
- The traumatic type of anomaly is more likely to occur as a result of premature loss of milk teeth or in the presence of bad habits.
- Treatment of a traumatic open bite is more effective during the formation of a temporary or intermittent bite.
Cross bite
One of the main signs of the presence of pathology is facial asymmetry. The anomaly can be one-sided or two-sided and form in the lateral or anterior region.
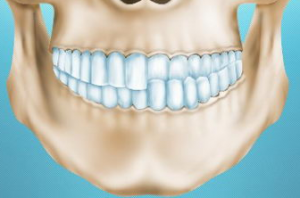
- Violation of chewing food. As a result of insufficient chewing, various diseases of the digestive tract can develop.
- The risk of periodontal disease increases.
- Pain and a crunch in the temporomandibular joint may appear.
- It is a problem when performing some dental procedures.
- The occurrence of impaired breathing and speech.
- The risk of caries increases.
Distal bite
It is an anomaly of the bite, which is characterized by the fact that during the closing of the teeth, the upper incisors are strongly advanced in the front direction with respect to the lower teeth.
The consequences of pathology:
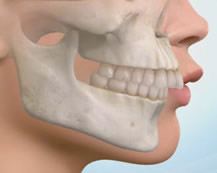
- The risk of caries increases.
- The swallowing process is disrupted.
- The occurrence of pain and a crunch in the temporomandibular joint when opening the mouth.
- There is a high risk of periodontal disease.
- There are difficulties when performing some dental procedures.
Mesial bite
Pathology is characterized by an increase in the size of the lower jaw compared with the upper.
Externally, the anomaly is manifested by the following symptoms:
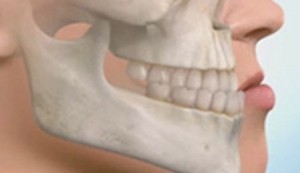
- The protruding chin, and the profile of the face has a concave appearance.
- With closed jaws, the lower incisors protrude forward.
The consequences of pathology:
- The function of chewing food is impaired.
- The shape of the face is distorted.
- Periodontal disease develops.
- Complications of the temporomandibular joint (crunch, pain, or clicking in the joint).
- There are problems with implantation, prosthetics or other dental procedures.
Is it possible to fix it?
Orthodontic treatment of any of the malocclusions is usually complex and quite long.
In this regard, do not neglect preventive measures that will help to form the correct bite in a child from a very young age.
Currently, any pathology of the bite is being successfully treated.
And the sooner the correction of malocclusion is started, the more successful the result will be.
A photo: nmalocclusion
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|