Prosthetics of deciduous teeth

Modern pediatric dentistry is a combination of modern methods of treatment and restoration of lost teeth.
Children's teeth, especially at an early age, are highly susceptible to decay.
An unfavorable environmental situation, poor nutrition, insufficient care for baby teeth, untimely seeking medical help leads to the fact that small patients get to the dentist already at the stage of advanced caries.
This leads to the fact that it is not always possible to preserve in full the destroyed teeth of the child. In this case, dental prosthetics come to the rescue.
Prosthetics of deciduous teeth in children very different from prosthetics in adults.
- In children, in contrast to adults, there are only 20 teeth that perform their basic functions.
- Premature loss of even one tooth is a noticeable defect for the child.
- Normally, the change of milk teeth occurs in the period from 6 to 12 years.
- Chewing teeth, sixth, seventh, and also wisdom teeth do not have milk predecessors and are formed as permanent.
Procedure for changing milk teeth
| Age | Teeth |
| From 6 to 9 years old | Central and side incisors |
| From 9 to 10 years old | First premolars |
| From 10 to 11 years old | Fangs |
| From 11 to 12 years old | Second premolars |
What happens with premature tooth loss
- The load on the remaining teeth increases.
- Standing next to the removed teeth, take its place and do not allow a permanent tooth to erupt normally.
- There is no bone growth at the site of the extracted tooth, which can create an obstacle to the erupting permanent tooth.
- Decreased bite height.
- Violation of diction.
- There are inconveniences during chewing food.
- The presence of a cosmetic defect, which is clearly visible during a conversation and a smile (with the loss of front teeth).
When required
Situations when prosthetics of primary teeth are necessary:
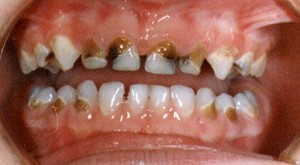
- Severe tooth decay with caries, not subject to restoration.
- Tooth injury (crown fracture, tooth root fracture).
- Fluorous tooth decay.
- Inflammation of the periosteum, requiring immediate tooth extraction.
- Loosening and tooth loss during periodontitis.
- Premature tooth loss.
- If there is a cosmetic defect after treatment as a result of caries or injury. This is especially important for the front teeth.
Video: “Prosthetics of deciduous teeth”
Dentures
Baby dentures allows you to maintain the beauty and health of teeth.
Giving preference to tooth restoration, it is possible to prevent their displacement and deformation of the dentition.
Prosthetic treatment allows you to preserve the functions of the teeth and normalize breathing, speech, tooth growth and jaw.
Kinds
Children's dentures are divided into: removable and non-removable.
These include:
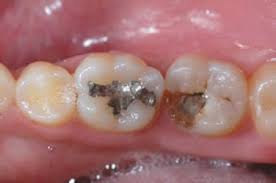
- TabsUsed on teeth with defects.
- Crowns are installed to cover the destroyed tooth crown. The tooth is prepared according to the usual method with preservation of the pulp.
- The pins are installed in the roots of the front teeth or fangs of the lower jaw.
- Bridge prosthesis.
- Fixed console.
- Laminar dentures: sliding and conventional. They have a large basis. Sliding plate prostheses, aligning the dentition, do not interfere with the growth of jaws and teeth.
Most often, removable structures and dental crowns are used for prosthetics of primary teeth.
A removable denture is made according to individual castings of the dentition.
The removable design often includes additional elements: screws, arcs, springs. As the patient grows, the designs must be replaced.
Tooth crowns
Indications:
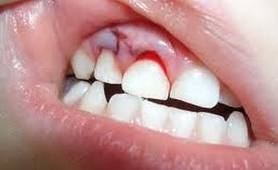
- Decay of deciduous teeth by caries by more than half.
- Complete tooth decay.
- Tooth injury.
- To restore a tooth with a removed nerve.
- Restoration of a tooth with active caries.
- Bruxism (night grinding of teeth).
- Restoration of permanent erupted teeth with a violation of the development of enamel.
Pros:
- Do not adversely affect oral hygiene.
- Durable.
- Prevent caries.
- Highly aesthetic.
- Replace the tooth and restore its function.
- Do not affect the physiological change of primary teeth, the tooth falls out with the prosthesis.
In children's prosthetics, two types of crowns are used:
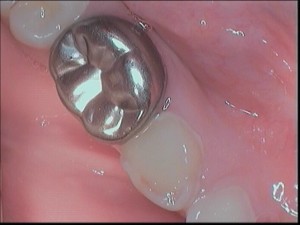
- Metal (made of nickel-chrome alloy or stainless steel). Used to restore chewing teeth.
- From composite materials (strip-crowns) for prosthetics of front teeth.
Milk teeth prosthetics are performed under local anesthesia.
Crowns made of metal are installed during one visit to the doctor; no more than 20 minutes are spent on the installation of strip crowns.
Prosthetics are performed without turning.
Requirements
Children's dentures should not impede the growth of the jaw bones and teeth.
Constructions should be:
- Simple and atraumatic.
- Made of lightweight, hygienic, hypoallergenic, harmless, resistant to various kinds of influences, not shrinkable and not swelling in a humid environment material.
- Aesthetic.
For the manufacture of prostheses use:
- Acrylate plastics.
- Chrome steel.
- Tin and silver based alloys.
- EI stainless steel - 95.