Direct veneers
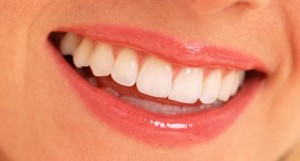
The main methods of tooth restoration with veneers are direct and indirect veneering.
Direct veneers are tooth pads made directly in the patient's oral cavity.
Typically, such veneers are made of composite materials that repeat the color and shape of the teeth, giving them high aesthetics.
Direct veneering of teeth is carried out during one medical appointment. Usually, it is used to eliminate defects in one or two teeth.
If it is required to correct defects of a larger number of teeth, it is better to install structures using indirect veneering.
Benefits
- In some cases, when installing direct veneers, it is not necessary to grind the teeth.
- The direct method of installing pads is quite simple and does not take much time.
- The manufacture of the patch is made in the patient's mouth and does not require a cast.
- There is no need to use painkillers.
- If the patient refuses to use the veneers or replaces them, it is possible to remove the cover, since the tooth under it will remain in its original form.
- Fixation of the lining requires a slight roughness, providing better adhesion of the adhesive to the tooth surface.
- It is possible to pre-select the shape and color of the veneer using a special program.
- Direct veneers are relatively inexpensive, their price two times less than indirect, made of ceramic.
The result obtained entirely depends on the skill of the dentist.
disadvantages
- Composite materials used in direct veneering require periodic correction and polishing, as they quickly fade and wear out.
- The increased abrasion of the pads.
- The increased fragility of vinyl records increases the risk of structural failure.
- Swelling of the composite material in a humid environment often causes hyingivitis, bleeding gums, irritation, depressurization of the edges of the lining, pigmentation of the border, making oral hygiene difficult.
All of the above disadvantages lead to a loss of aesthetics and require replacement of the restoration.
The service life of direct veneers, with sufficient care and compliance with functional load standards, ranges from three to 8-9 years.
When install
Direct veneers are indicated for installation in the following cases:
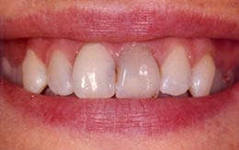
- With age-related changes in the teeth.
- If, as a result of an injury, the edge of the tooth has broken off.
- With tooth wear.
- If there is an uneven contour of the necks of the teeth.
- With underdevelopment of teeth.
- If there is a large gap between adjacent teeth.
- As an alternative to teeth whitening.
- If you want to change the group affiliation of the tooth.
- In the presence of crooked teeth.
- If the dentition is not even.
- The presence of spots or yellow plaque on the surface of the enamel.
- If the tooth has old fillings, giving the teeth an unaesthetic appearance.
Direct veneers, as well as indirect ones, have a number of contraindications for installation:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Allergic reactions to some of the ingredients that make up the pads.
- Malocclusion.
- Periodontal disease.
Installation steps
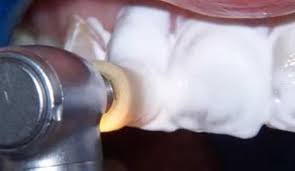
- The surface of the tooth is cleaned of plaque.
- The necessary shade of the future restoration is selected.
- Grinding a thin layer of enamel.
- Enamel etching with acid.
- Application of the composite to the surface of the prepared tooth.
- Formation of veneer and its final processing.
- Polishing the finished restoration.