Deep bite
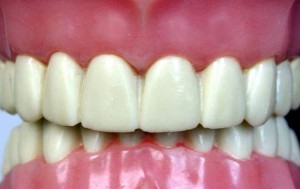
Deep bite is the most common defect in the closure of teeth, in which there is overlapping of the mandibular incisors with the upper incisors.
With a deep bite, the incisors of the upper row overlap the crowns of the incisors of the lower row by more than a third.
In some cases, this anomaly may be present in the lateral region of the dentition.
In dentistry, the term “deep bite” can be replaced by the terms “deep incisal (frontal) overlap”, “traumatic bite”, “deep incisal occlusion”, “declining occlusion”.
Causes
The formation of a deep bite can contribute to genetic, intrauterine and postpartum factors.
Among the main reasons can be identified:
- Congenital malformations. Most often, a malocclusion can be congenital and inherited along with structural features of the facial skeleton, including the dentofacial system. Anomalies such as cleft lip, cleft palate also contribute to malocclusion.
- Chronic diseases of the mother. A deep bite in a child can be the result of chronic diseases such as endocrine disorders, metabolic diseases, anemia, and viral diseases.
- The pathological course of pregnancy and fetal developmental disorders.

Finger sucking causes malocclusion - Metabolic diseases affecting the growth and development of the skeletal system.
- Violation of the period of teething and change of dairy constants.
- Anomalies of the teeth and attachment of the frenum of the lips and tongue. The presence of diastema, multiple caries, partial adentia.
- Injuries and osteomyelitis of the jaws.
- Diseases of the ENT - organs and digestive system.
- Congenital and acquired defects of the musculoskeletal system.
- Anomalies of breathing, swallowing, sucking, speech.
- Bad habits: prolonged use of a dummy, sucking fingers, etc.
Classification
The criterion for the differences between a deep bite, a traumatic bite and a deep incisal overlap is the localization of the cutting-tubercular contact.
In orthodontics, three degrees of deep bite are distinguished (depending on the amount of overlap of the central incisors):
- In the case of a significant overlap of the lower incisors by the upper ones, and the absence of a cutting-tubercular contact, we are talking about a deep bite.
- A deep (excessive) incisal overlap is indicated if there is contact between the teeth of the lower jaw and the palatine tubercles of the upper teeth.
- If the cutting edges of the lower teeth are in contact with the palate or gum, then such a bite is deeply traumatic.
The above forms of occlusion can be considered as stages of the pathological process.
For example, with pathological abrasion or tooth extraction, a deep incisal overlap can be transformed into a deep bite, and he, in turn, can be transformed into a deep traumatic one.
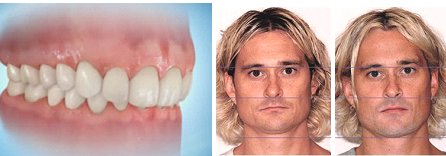
There are several varieties of deep bite:
- Distal deep bite.
- Neutral deep bite.
Signs of a distal bite
- The upper teeth overlap the lower ones by the size of the entire crown.
- During a smile, exposure of the upper front teeth to the neck occurs.
- Visually, the face is shortened and the underdeveloped lower jaw.
- The chin is normal in shape or slightly sloping.
Signs of a neutral deep bite
- The upper incisors overlap the lower ones by the size of the entire crown.
- The chin is not changed and has the usual shape.
- The lower part of the face is slightly shortened or equal in length to its middle part.
Symptoms
Anomaly of occlusion is characterized by the following symptoms:
- With a deep bite, periodontal disease first of all suffers, which is manifested in frequent inflammation of the gums, trauma to the teeth of the oral mucosa, and loosening of the teeth.
- Facial signs of a deep bite are characterized by a shortened lower part of the face, as well as an ugly lip position.
- It is often difficult for patients with malocclusion to bite off food and chew.
- Often there is increased tooth wear and speech impairment.
- A decrease in the oral cavity, which contributes to disruption of the swallowing process and the development of improper breathing.
Video: “Installation of lingual braces”
Treatment
In order to choose the right tactics for treating anomalies, it is necessary to take into account the patient's age and the cause that caused the development of the wrong bite.
Treatment of a deep bite, both in children and adults, can be carried out using special orthodontic appliances. This involves: plates, mouth guards, braces and other devices.
Correction of a deep bite is more effective to begin during the period of teething, or when the milk teeth are constant or at the beginning of the eruption of the second molars.
Features of treating children
Treatment of children, starting from the age of two and including six-year-olds, implies the following measures to prevent the development of anomalies:
- The inclusion of solid foods (fruits, vegetables) in the diet.
- Timely treatment of caries and prosthetics of teeth lost ahead of time for any reason.
- Trimming the frenum of the lips and tongue, if necessary.
- The exception in a child is bad habits.
In the presence of a deep distal bite in a child, the treatment plan for the anomaly is somewhat complicated and includes:
- Expansion of the upper and lower dental arches.
- Correct placement of the front teeth.
- Mesial movement of the lower jaw.
- The height of the bite is leveled.
Moreover, the entire process of bite correction is limited to the use of the plate and myogymnastics, which will contribute to the proper growth of the jaw.
After the child reaches the age of six, when the change of milk teeth begins, the anomaly is treated with mouthguards, retainers, removable vestibular plates or other devices.
After the child is 12 years old, lingual and vestibular braces are used to correct a deep bite. Moreover, lingual braces are able to quickly correct the anomaly.
Features of the treatment of adults
In adults, the use of myogymnastics and removable devices is not effective.
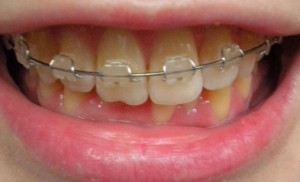
- To eliminate malocclusion, bracket systems are used.
- In the case when the patient has no desire or opportunity to correct the bite with the help of braces, they can be replaced with veneers. At the same time, the appearance of the patient with malocclusion changes for the better. But, veneers cannot eliminate the root cause of the anomaly and therefore are only a temporary solution.
- Implant prosthetics is a fairly effective way to get rid of incisal overlap, which takes much less time than braces. But it should be noted that implantation is an expensive procedure that has a lot of contraindications.
Effects
A deep bite can cause the following negative consequences, which are expressed in the following:
- Impaired speech, breathing.
- Injury to the oral mucosa.
- Difficulty chewing, swallowing.
- Increased tooth abrasion.
- Lack of aesthetics of appearance.
- The tone of the masticatory muscles is impaired due to increased tooth erasure.
- The presence of pain, clicking, crunching in the temporomandibular joint.
- A deep bite may be accompanied by other malocclusions.
- One of the serious complications of deep bite is bruxism.
- Frequent headaches.
Prevention
Prevention measures are as follows:
- Natural feeding of the child.
- Timely getting rid of a baby from a dummy, as well as from such bad habits as sucking toys, fingers and various objects.
- Timely treatment of caries.
- Prevention of violation of posture.
- Prevention of chronic respiratory diseases, rickets and other somatic diseases.
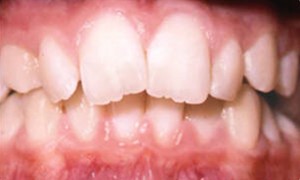
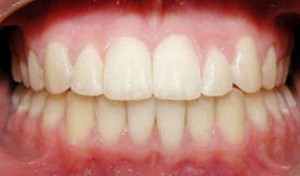
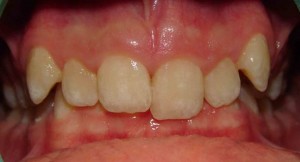
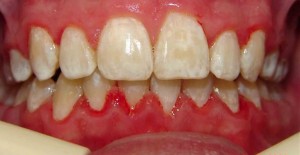
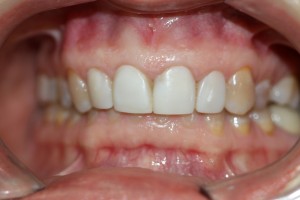
Before and after photos
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |