Progenic Bite
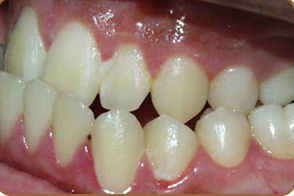
Types of occlusion of teeth are determined by the characteristic closure of the dentition in the position of central occlusion.
One of the types of physiological closing of teeth is a progenic bite, which is characterized by the fact that at the moment of closing of the teeth there is a slight extension of the lower jaw forward.
Based on a number of signs, a progenic bite can be physiological or pathological.
Correct Progenic Bite
- With a physiological bite, the extension of the lower jaw is negligible.
- In this case, the presence of multiple contacts between the front and side teeth of the upper and lower dentitions is noted.
In this case, the bite is considered normal and correction is not required.
A physiological or correct bite is considered to be a type of jaw occlusion that provides:
- Optimal functioning of the dentition.
- The absence of a high load on the temporomandibular joint.
- Stability and esthetics of the dentition.
- Health and periodontal protection.
Symptoms of abnormal development
The clinical picture of the anomaly is quite diverse.
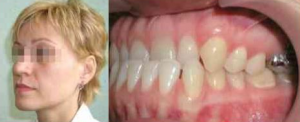
- Facial and intraoral signs of the development of pathology in the temporary bite are weakly expressed, compared with the period of a removable or permanent bite.
- A pathological progenic bite is characterized not only by the lack of contact between the teeth, but also by functional disorders of the dentition.
- Aesthetic changes are not excluded due to violations in the maxillofacial system.
Pathology of the bite can be observed at different ages and requires orthodontic treatment.
The following forms of correlation of dentitions are distinguished: dento-alveolar and gnatic.
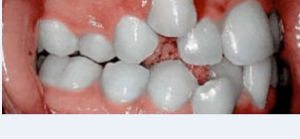
- The gnatic form of progeny is a consequence of abnormal development of facial bones.
- The dentoalveolar form is formed when the position of the teeth in the alveoli of the jaw bones is disturbed.
Each of the forms of a progenic bite can be combined with an anomaly of displacement of the lower jaw.
Kinds
By localization, progeny can be general or partial:
- General Progenia - characterized by a mismatch in the closure of the lateral and front teeth.
- Partial - the presence of non-closure in the area of only the frontal or lateral teeth.
The anomaly can be with or without displacement of the lower jaw.
Depending on the cause, a false and true progeny is distinguished:
- The development of a pathological progenic bite is based on a true increase in the lower jaw.
- With a false form of malocclusion, frontal progeny is observed, as well as forced.
Causes
The development of a pathological bite can be associated with a variety of reasons.
Is progeny inherited?
Unfortunately, some types of pathology, including progenic bite, can be hereditary.
Among the factors contributing to the appearance of anomalies, there are:
- Diseases of the pregnant woman, which can cause the development of anomalies of the dentofacial system of the fetus.
- Congenital not fusion of the palate and alveolar processes.
- Lack of frontal upper teeth.
- Atypical position of tooth primordia.
- Late change of teeth.
- Premature loss of primary teeth.
- The presence of oral breathing in a child with hypertrophy of the tonsils.
- Improper position of the baby's head during sleep.
- Imperfect tubercles of fangs of milk teeth.
These factors contribute to the disruption of the physiological balance of the facial and chewing muscles, which causes an increased effect on the bone of the lower jaw, leading to stimulation of its growth and development.
Treatment
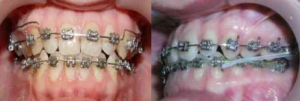
The process of orthodontic treatment of progenia should:
- Stimulate the growth and development of the upper jaw.
- Restrain the growth of the lower jaw and be directed to its distal movement.
- Correct the wrong position of the teeth in a row.
- Normalize the height of the bite.
During the temporary bite, treatment and prevention of pathology should contribute to the harmonious development of dental arches and the removal of obstacles to the distal movement of the lower jaw.
Such measures are:
- Normalization of the processes of respiration, swallowing and tongue functions.
- Timely rehabilitation of the oral cavity.
- Getting rid of bad habits.
- Myogymnastics classes.
- The use of an extraoral bandage.
During the development of a removable bite in a child, orthodontists begin to carry out treatment using intraoral devices and devices: cap, plates, arches.
Permanent progenic bite to fix fixed structures, such as braces.
Unlike children, in adults it is no longer possible to influence the growth and development of bones by purely orthodontic methods.
Attempts to correct the anomaly using only orthodontic methods can not only not solve the problem, but also cause morphological and functional complications.
In this regard, to correct pathological progeny during the period of a permanent bite, complex treatment and surgical intervention are successfully used.
Cost
The cost of correcting the anomaly depends on the method and designs with which the treatment is carried out.
| Type of apparatus | Prices (in rubles) |
| Trainers | 8000 |
| Removable plate | 13000 |
| Bracket system | From 10000 |
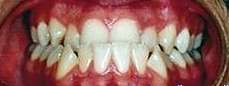
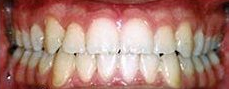
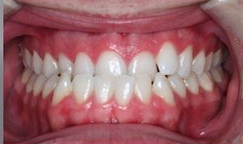
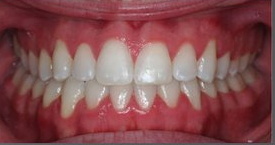
Photo: before and after
 |
 |
 |
 |
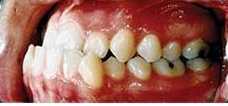 |
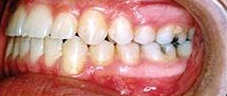 |