Cross bite
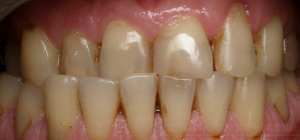
Cross bite is a type of anomaly characterized by a displacement of the lower jaw relative to the upper in the horizontal plane.
In the presence of this pathology, the dentition of the upper and lower rows intersect.
With a cross bite, asymmetric development of the bones of the face and temporomandibular joints is observed.
Anomaly in the development of occlusion can lead to impaired speech, chewing, breathing, and traumatic occlusion.
Correction of the cross bite, which is a very long and laborious process, must be started at a very young age.
Classification
Cross bite can be observed in the anterior jaw or in the side sections. In orthodontics, the following clinical forms of malocclusion are distinguished: buccal, lingual and buccal-lingual.
Buccal bite
- The defect is characterized by a violation of the occlusion of the posterior teeth, which complicates the process of chewing food.
- A buccal bite can be either with displacement of the jawbone, or without displacement.
Lingual bite
- The anomaly is characterized by the closure of the lateral teeth by antagonists and even the lack of contact caused by the narrowing or expansion of the dentition of the upper jaw.
- A lingual bite can be either one-sided or two-sided.
Buccal lingual bite
- Gnatic bite, which is characterized by a narrowing or expansion of the base of the jaw.
- Tooth alveolar bite. The anomaly is characterized by underdevelopment or strong development of dentoalveolar jaw arches.
- Joint type of bite, in which there is a shift of the lower jaw to the side.
Video: “Bite Correction”
Causes
Cross bite can develop for various reasons.
The most common causes include:
- Adverse heredity. Often a child receives this anomaly by inheritance from parents.
- The presence of inflammatory processes that violate the growth and development of the jaw.
- Diseases in children that have an adverse effect on phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
- Inconsistent activity of chewing muscles.
- Violation of the bookmarks of the primordia of the teeth.
- Untimely loss of primary teeth.
- Respiratory failure through the nose.
- Hemiatrophy of the muscles of the face.
- Bruxism.
- Improper position of the child during sleep (putting hands or cam under the cheeks).
- The presence of bad habits, such as sucking fingers, toys or biting lips, propping up your cheeks with your fist.
- After receiving facial injuries.
- The presence of congenital clefts of the soft palate.
- The consequences of malocclusion
If you do not take measures to eliminate this pathology, then the development of an anomaly can cause complications such as:
- Disruption of the digestive system as a result of defective chewing of food.
- The occurrence of caries and periodontal disease.
- Frequent sore throat in children and adults.
- Difficulty breathing.
- The presence of a number of complexes associated with external data and speech.
According to some scientists, a cross bite can cause frequent headaches and high blood pressure.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture of the anomaly is quite diverse and depending on the type of defect, the symptomatology has its own characteristics.
Cross bite is characterized by the following symptoms:
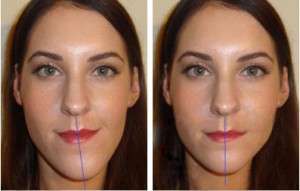
- Asymmetry of the front of the skull.
- Restrictions of the movements of the lower jaw, which lead to poor chewing, and in some cases to periodontal disease.
- Displacement of the lower jaw is observed with wide opening of the mouth.
- In addition to the horizontal shift of the lower jaw, its diagonal shift can be observed.
- Often there is a violation of the shape of the face: a shift of the chin to the side and drooping of the upper lip, while on the opposite side there is a flattening of the lower portion of the face.
- Chewing function impairment. Often observed biting cheeks.
- In the presence of a lingual cross bite, limited movement of the lower jaw is noted.
- Violation of pronunciation of sounds.
An important role in the diagnosis of cross bite is played by an X-ray examination of the temporomandibular joints.
Anomaly correction
When treating occlusion anomalies, the patient's age, cause of occurrence, severity of the disease, and also a type of pathology are taken into account.
Treatment of malocclusion anomalies, regardless of its shape, is necessary at any age.
The following measures help correct the bite in children with a milk and replaceable bite:
- Eliminate bad habits.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity and improvement of the nasopharynx.
- Grinding of tubercles of milk teeth, which interfere with lateral movements of the lower jaw bone, is carried out.
- As soon as the first signs of development of a cross bite occur, the doctor applies the separation of the dentition. In the presence of a significant narrowing of the dentitions and jaws, expansion plates with screws and springs are prescribed.
- In the period when there is intensive growth of the jaws, activators, a regulator of Frenkel functions are used.
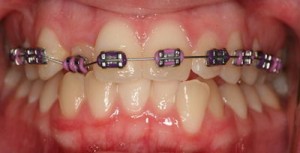
Treatment of occlusion in adults and adolescents consists in the use of special orthodontic appliances, the task of which is to expand or narrow a separate section of the dental arch, normalize the tone of the masticatory muscles, and put the lower jaw in the correct position.
For the treatment of adults and adolescents, a bracket system is usually used. How long the treatment will last, and how long it will take to wear braces when correcting a bite, depends on the severity of the anomaly and the patient's age.
In the presence of pronounced deformities, surgical intervention is often recommended.
More often, surgery is necessary for people with congenital, hereditary pathology.
- After correcting the bite, a retention device must be used to save the result.
- Most often, removable plates are used, which they put on at night.
- In this case, it is necessary to follow all the recommendations of the orthodontist in order to preserve the result longer.
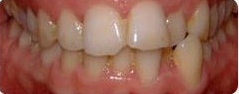
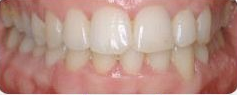
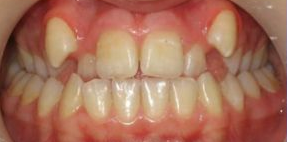
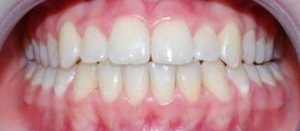
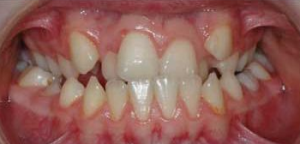
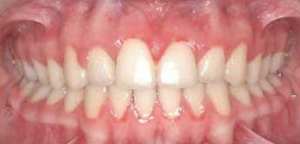
Photo: before and after
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |