Open bite
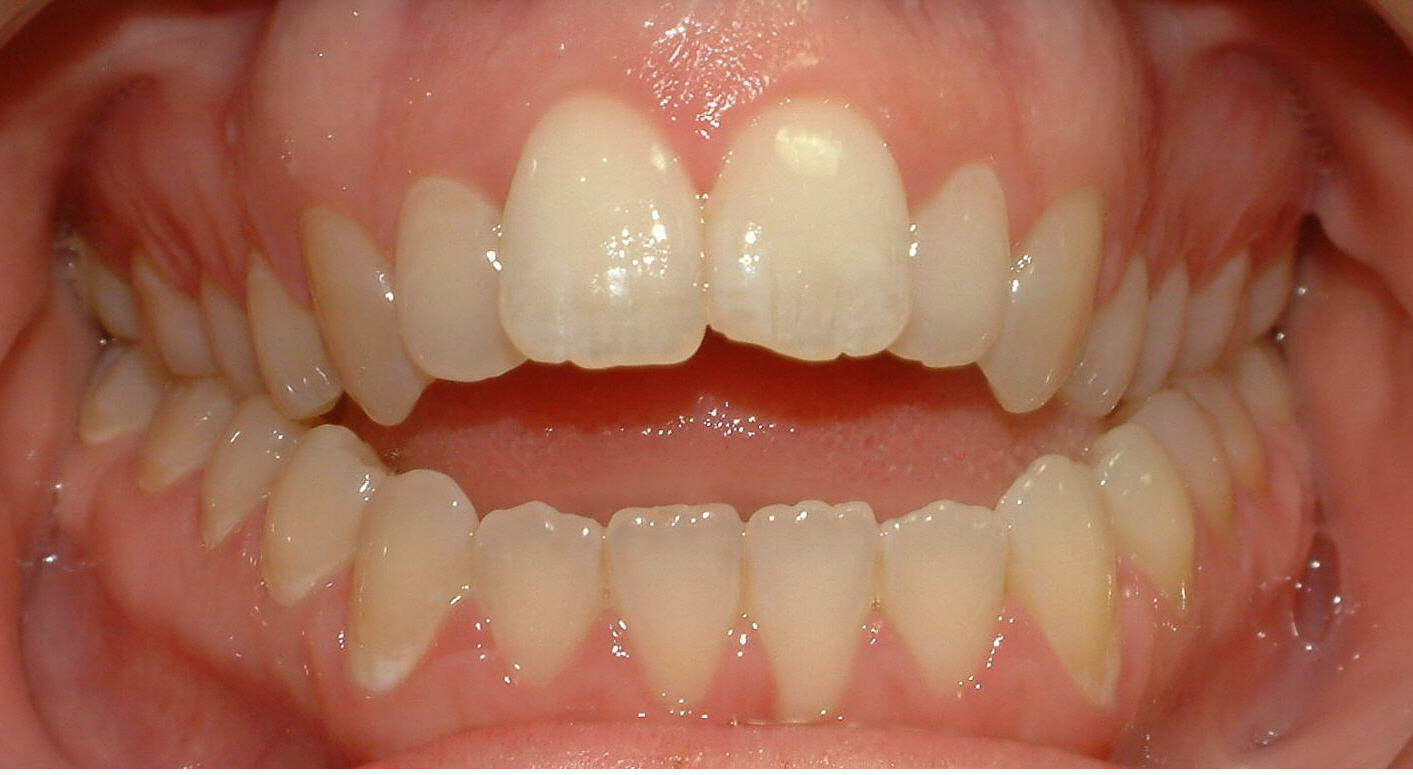
An open bite is a pathology in which there is no complete closure of the upper and lower teeth. This is one of the most severe forms of anomaly encountered in orthodontics. An open bite is more common in children.
- In adults, the incidence of abnormalities does not exceed 2% of all patients.
- In 20% of cases, pathology is found in babies under the age of one year.
- In a six-year-old child, the chances of having an open bite fall to 6% and sharply decrease by twenty-seven years.
In addition to the aesthetic aspect, an open bite carries a potential health hazard:
- It can be a cause of speech impairment and provoke the development of ENT diseases.
- Incomplete closure of the jaws contributes to insufficient chewing of food, the consequences of which lead to disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Kinds
There are several types of open bite:
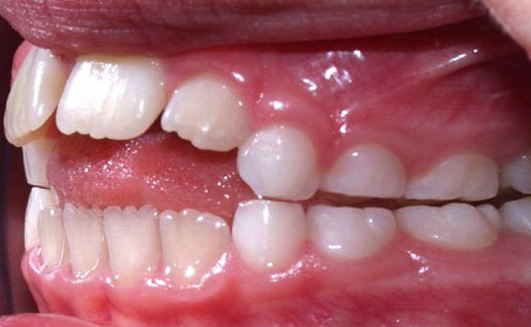
- Front open bite. This type of anomaly is most common. The front open bite may manifest independently or be associated with other diseases.
- An open lateral bite, which is less common, can be one-sided or two-sided.
For a long time, orthodontists have not been able to provide effective treatment for such patients.
To date, dentistry has several methods for correcting occlusion.
From the point of view of the cause, two types of anomalies are distinguished:
- True or rickety open bite.
- False or traumatic bite.
Rickety (true) open bite
This is the most severe form of malocclusion. With a true bite, treatment is quite difficult and very slow, since there are changes in the structure of the jawbone. Symptoms
- A patient with this anomaly has difficulty breathing and speech.
- There is no possibility of biting off food, it is difficult to chew it.
- The patient's face is deformed, the mouth is open, as a result, the mucous membrane of the mouth constantly dries up.
Traumatic open bite
This type of bite is more characteristic of primary teeth.
- An open bite can form as a result of the loss of one or more teeth or as a result of such a bad habit as sucking fingers or toys.
- If the abnormality was not corrected before the appearance of permanent teeth, then more complex orthodontic treatment may be required.
- In addition, the help of a periodontist may be required.
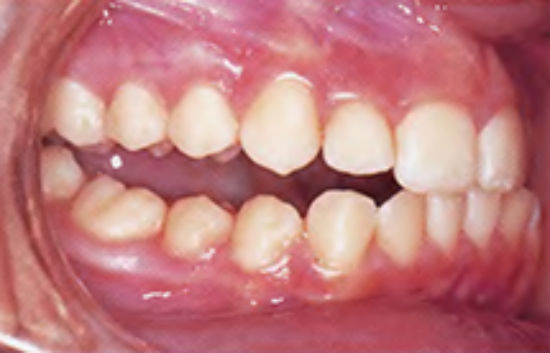
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is based on the following symptoms:
- The process of biting off and chewing food is difficult. The main role belongs to the language, which takes part in the formation of the food lump.
- There is a violation of articulation and difficulty in pronouncing certain sounds.
- Infant or infantile swallowing is observed.
- The mucous membrane of the mouth is often overdried, as breathing through the mouth is difficult.
- Lips are most often tightly closed to hide the defect.
The severity of symptoms and the degree of its manifestation depends on the distance between the teeth:
- With an open type of bite of 1 degree, the distance does not exceed - 5 mm.
- With 2 degrees of severity - 9 mm.
- With 3 degrees - 9 or more mm.
The diagnostic sign of an open bite is also the number of open teeth.
- If an abnormality develops under the influence of bad habits, a malocclusion may become cross-sectional or asymmetric.
- Cross bite, for example, can be the result of such a bad habit as sucking the thumb in infancy.
- An ordinary dummy can also cause the formation of an open bite in a child. Therefore, the process of selecting a dummy must be very thorough.
Video: “Bite correction”
Causes
Among the reasons that influence the formation of an open bite, we can name the following:
- Adverse heredity.
- Congenital pathology of the fetus.
- Past viral or infectious diseases during pregnancy.
- Carried by a child rickets.
- The presence of bad habits in the baby, such as, for example: sucking toys, fingers, etc.
- Uncomfortable position of the child’s head and torso during sleep (head tilting).
- Jaw injuries.
Factors contributing to the development of anomalies:
- Inadequate exposure to the sun.
- Malnutrition of the child.
- Inadequate motor activity, neglect of exercise.
- The presence of dysbiosis.
- When conducting anticonvulsant therapy, as a result of which the excretion of vitamin D from the body is enhanced.
- Violation of metabolic processes in the body.
- Diseases of the kidneys and liver, in which the excretion of vitamin D is enhanced.
- Bad ecology.
Before starting the correction of the bite, it is necessary to eliminate the above factors.
Treatment
It is advisable to begin treatment of an open bite in children under the age of three with measures aimed at preventing the occurrence of anomalies. At an early age, prevention is a fairly effective measure. Dentists recommend:
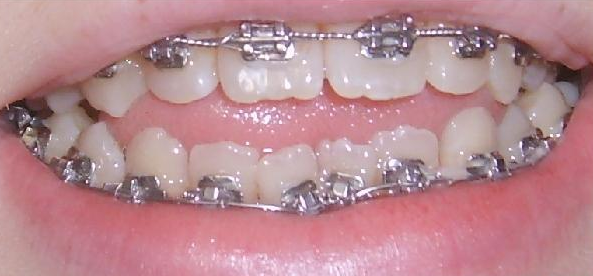
- At the first stage, during the formation of a milk bite in a child, it is necessary to eliminate bad habits, teach the child proper breathing through the nose, and normalize the position in the mouth of the child’s tongue.
- Perform myogymnastics aimed at strengthening the circular muscles of the mouth.
- Include solid foods in your child’s diet.
- Timely oral sanitation and treatment of deciduous teeth.
- Orthodontic treatment with cap and trainers until the child reaches the age of thirteen. These measures are aimed at correcting the growth and development of the jaw bones.
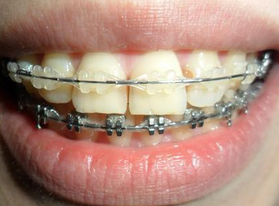
- During the formation of a permanent open bite, the most effective is the correction of the anomaly with braces.
- In complex neglected cases, malocclusion can only be corrected surgically.
Apparatus used for treatment
The following structures are most often used to correct anomalies:
- A plate with a shutter for the tongue.
- Devices that impede the location of the tongue between the dentition.
- At the end of the replacement bite, bracket systems are used.
No less effective is the use of extraoral constructions.
Prevention
Prevention of malocclusion in a child should start from a very early age.
For this, doctors recommend the following actions:
- Monitor the baby’s breathing. It is necessary to timely treat diseases of the ear, throat and nose. Do not let the child breathe through the mouth.
- Visit your dentist regularly and have your mouth cleaned up in a timely manner.
- Prevention of rickets.
- if there is evidence, conduct timely correction of the frenum of the tongue.
- In the presence of speech defects, visit a speech therapist.
- perform exercises aimed at the proper development and growth of the jaw bones and muscles of the mouth.
- Timely elimination of bad habits in a child.
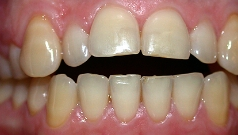
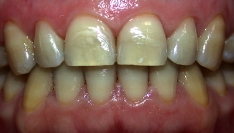
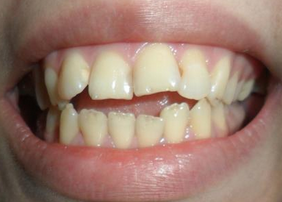
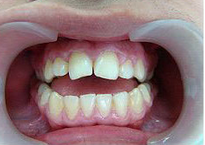
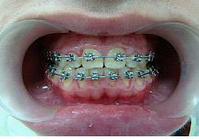
Photo: before and after treatment
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |