Numbness after dental implantation
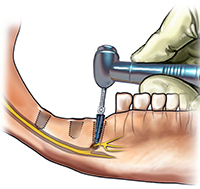
During dental implants, local anesthesia is most often used.
When using it, the sensitivity may be absent for three to five hours, which is the norm.
If after the expiration of the indicated time the numbness does not disappear, then this may indicate damage to the lower branch of the trigeminal nerve located in the mandibular canal.
Therefore, when planning the site of implantation, the doctor must bypass this anatomical formation during their installation.
Numbness after dental implants is a rather rare postoperative complication that occurs solely due to the fault of the doctor.
Causes of mandibular nerve damage
- The main reason is insufficient study of the features of the jaw at the preparatory stage of the operation, as a result of which the implants and the place of their installation were incorrectly selected.
- During anesthesia, a nerve injury with a needle is possible.
- The length of the implant is too long: at the stage of its installation, nerve damage can occur, both by the implant itself and when using bone drilling tools.
Symptoms of Nerve Damage

- Discomfort in the lower jaw.
- The sensitivity of the lower part of the face is impaired.
- Numbness of the chin, teeth, gums, lips, tongue, cheeks.
- Violation of facial expressions.
- Difficulties in eating food, carrying out procedures: brushing, shaving, applying makeup.
- Violation of diction.
- Presence of soreness.
- Increased salivation.
In severe cases, you can even choke while eating and drinking drinks.
Stages of Nerve Damage
- Neuropraxia - the presence of minor damage to the mandibular nerve. At this stage, there is a slight numbness that goes away after one to two months.
- Axonotmesis is a partial but more serious nerve damage. In the presence of such damage, pain sensations join. Numbness disappears on its own in no less than two months.
- Neurotmesis - severe damage to the mandibular nerve, and a scar remains on the damaged area. The state of numbness and pain does not go away for three months. Attempts to restore a nerve are not possible even surgically.
What to do
- If after implantation, there is a loss of sensitivity in any part of the face or oral cavity, it is urgent to consult a doctor who performed the operation.
- The treatment should be carried out by a neurologist, dentist and physiotherapist.
- Timely diagnosis and determining the degree of damage to the mandibular nerve can play an invaluable role.To do this, a control picture is assigned, allowing to assess the position of the implant with respect to the mandibular nerve.
- It is important to get quality treatment on time. Complex physiotherapy is prescribed, aimed at restoring the sensitivity and conductivity of the damaged nerve.
- With timely treatment, it is often possible to restore sensitivity with the help of medications and avoids surgical intervention.
How to prevent nerve damage
Quality preoperative preparation:
- The appointment of three-dimensional images of the jaw, necessary to assess the quality of bone tissue, the location of blood vessels and nerves.
- Correct determination of the size of the implant and the place of its implantation.
- If the nerve is too close, protect it from damage.
Before implantation, the surgeon must inform the patient about the risk of a possible complication.