Removable plate prostheses
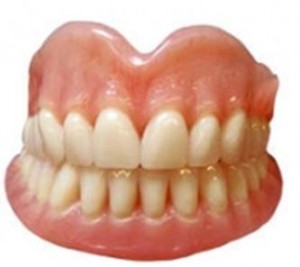
Removable plate prostheses are designs designed to restore chewing function.
They are not physiological devices, since during chewing, the load is transferred to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, and through it to the alveolar processes and jaw bone, as well as the palate, which is not physiological.
Over time, when using such structures, atrophy of bone tissue occurs.
A removable plate prosthesis consists of:
- Basis made of plastic. It connects all parts of the structure, transfers and distributes the load on the gum when chewing.
- Artificial teeth that are attached to the base of the prosthesis. They are made of plastic and delivered in a set consisting of teeth of one color and a certain shape.
- Clasps designed to fix the structure to the abutment teeth (in the case of a partial denture). Hooks are made of round wire. When fixing, the prosthesis presses its tooth to the patient’s tooth, thus improving attachment.
Indications
The use of a removable laminar denture is indicated in the following cases:
- If there are defects in the dentition, which is not possible to restore the bridge structures.
- With the simultaneous removal of a large number of teeth.
- If one tooth is missing.
- In the absence of several teeth.
- As a splinting construction for strengthening teeth.
- If you are allergic to metal.
- If there are contraindications for dental implants.
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications are determined by the general somatic state, as well as the properties of the structures:
- The presence of an allergic reaction to plastic.
- Diseases of the oral cavity that are untreatable.
- Schizophrenia.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Patients of certain professions: singers, broadcasters, lecturers, etc.
Relative contraindications include the following conditions:
- Acute inflammatory disease and acute viral infection.
- Chronic infections in the acute stage.
- After a recent heart attack or stroke.
- Tuberculosis, actinomycosis.
- Periodontal disease and periodontitis.
- Malocclusion.
Kinds
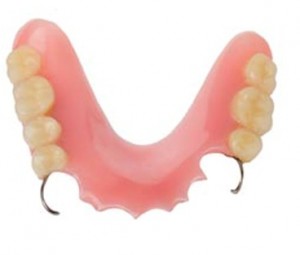
- Removable plate prostheses can be of two types: full and partial removable structures.
- Previously, dentures were made of rubber, but in the middle of the last century they were replaced by structures made of acrylic plastic, which for a long time was the only material used to make removable dentures.
- Currently, nylon, polyurethane and other modern materials have also been used for removable prosthetics.
- According to the method of fixation, prostheses are divided into: structures on suction cups, to clam fixation, on micro-locks (attachments) and prostheses on implants.
Partial removable
A partial removable laminar denture is used to restore one or more teeth, as well as in the presence of an end tooth defect. They are made of plastic or nylon, and fixed to the teeth with the power of clasps or attachments.
Full removable
They are used in the complete absence of teeth, when they are the only solution to restore the functionality and aesthetics of the dentition.
On the upper jaw, the structure is fixed due to the suction effect more reliably than on the lower jaw. For this reason, dentists seek to preserve at least part of the teeth on the patient’s lower jaw, which could become a support for the clasp structure.
disadvantages
- The basis of the prosthesis, covering a hard palate, contributes to the violation of the perception of taste and temperature.
- When using the design, its owners feel discomfort associated not only with eating, but also when talking.
- There is a violation of diction, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is irritated, there is a vomiting reflex.
- The size of the design basis depends on the severity of the arch of the hard palate, the number of teeth remaining in the oral cavity, the degree of atrophic processes of the jaw and alveolar processes.
- The more teeth are preserved, the smaller will be the size of the basis, and, conversely, with a small number of teeth, the basis of the structure will be larger.
- Bent clasps, adhering tightly to natural teeth and injuring them, can cause abrasion of enamel, loosening of supporting teeth and inflammation of the gums.
- The basis of the design can injure the gum, and therefore, immediately after the manufacture of the prosthesis, it may require repeated correction.
- Artificial teeth made of plastic are quickly erased.
Benefits
- The advantages of designs include their ease of manufacture and low cost.
- The disadvantages of the design basis prompted dentists to create a prosthesis of a less massive size and replace plastic with metal. Thus, the idea of creating arch prostheses was born.
For a long time, removable plate structures were almost the only alternative to a toothless oral cavity.
However, modern dentistry almost completely abandoned the use of such products.
The reasons for refusing removable plate prostheses are as follows:
- Nonphysiological. It manifests itself in the fact that when chewing food, pressure is transmitted to the gum, and then to the bone, which subsequently leads to deformation and atrophy of bone tissue. As a result of such changes, the fixation of the prosthesis worsens and further prosthetics are difficult.
- Clammer, putting pressure on the teeth, can lead to loosening and further loss.
- Discomfort when using. When using the design, diction is disturbed, gums are injured, and pain occurs. Designs may fall out of the mouth, food particles clog under the prosthesis.
- Short service life. A removable laminar denture can serve its owner on average 2.5-3 years. The design does not break, although the teeth can grind very much. The prosthesis ceases to correspond as a result of the atrophic changes in the bone tissue. If you use this design, then its detrimental effect on living teeth and jawbone only increases.
- Insufficient strength of the plate prosthesis due to the low quality of the material.
Video: “So do artificial teeth”
Manufacture
Thanks to modern plastics processing technologies, the manufacture of a complete removable laminar denture was made possible not only by compression molding.
If the laboratory has special equipment, then the design basis can be performed in the injection molding technique.
In this case, the manufacture of the prosthesis will cost more, but the design will provide the patient with a longer result of the prosthetics.
Manufacturing steps
The manufacture of removable structures in the complete absence of teeth consists of the following steps:
- Inspection and examination of the patient. Establishing diagnosis. Selection of the type of prosthesis.
- Jaw casting using standard spoons and impression mass.
- Casting of models in the dentist’s office, if the impression was taken with the impression mass, or in the laboratory, if the impressions were taken with plaster.
- Fabrication of a design basis with wax occlusal rollers in a laboratory.
- In the doctor’s office, the central ratio of the jaws is determined.
- Strengthening models in an articulator or occluder and making a wax structure in a dental laboratory.
- Verification of the wax structure in the patient's oral cavity.
- Final modeling and replacement of wax with base material, polymerisation of plastic.
- Finishing, grinding, polishing the finished structure.
- Fitting the prosthesis and giving it to the patient.
Compliance with the manufacturing sequence of the design ensures the quality of the manufactured prosthesis.
Only close interaction with the dentist and the accuracy of the dental technician in the process of work are able to ensure successful prosthetics.
Fix
- Failure of removable plate prostheses is not uncommon.
- Most often, plate structures break in the midline.
- The basis for removable dentures is repaired by gluing in a dental laboratory.
If for some reason the prosthesis base becomes unusable, regardless of what material it was made of, then, unfortunately, if the failure occurred more than two times, a complete replacement of the structure may be required.
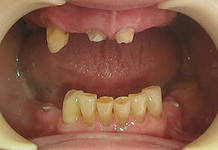
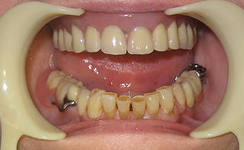
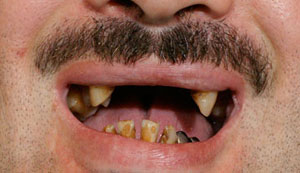
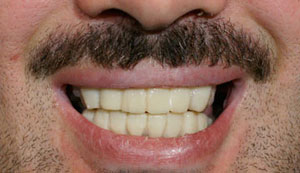
Photo: before and after
 |
 |
 |
 |
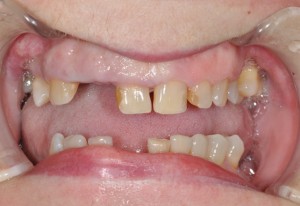 |
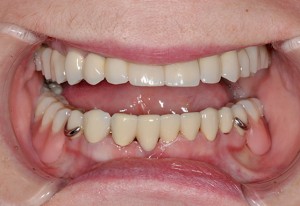 |